Package Development
A Note of Facades
When writing a package you will not have access to Laravel’s testing helpers. If you would like to be able to write your package tests as if you are using Laravel you may use Orchestral Testbench
https://github.com/orchestral/testbench
What is a Facade
https://www.sitepoint.com/how-laravel-facades-work-and-how-to-use-them-elsewhere/
A facade is a class, wrapping a complex library to provide a simpler more readable interface.
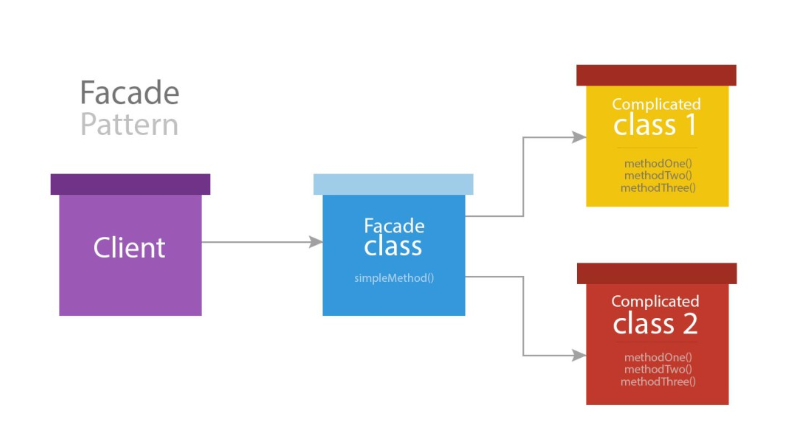
Facades in Laravel
A class which provides static-like interfaces to service inside the container.
In Laravel, all services have a facade class.
Package Discovery
app.php providers option is a list of service providers what should be loaded.
When someone installs your package you want your service provider to be included in this list.
This can be done in the extra section of your package’s composer.json file.
You may also list any facades which you would like registered.
Service Providers
Are the connection points between your package and Laravel. A service provider is responsible for binding things into Laravel’s Service Container and informing Laravel where to load package resources susch as views, configuration and localization files.
They extend Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider and contain register and boot.
Resources
Configuration
Get copied with vendor:publish
public function boot()
{
$this->publishes([
__DIR__.'/path/to/config/courier.php' => config_path('courier.php'),
]);
}
Routes
public function boot()
{
$this->loadRoutesFrom(__DIR__.'/routes.php');
}
Migrations
public function boot()
{
$this->loadMigrationsFrom(__DIR__.'/path/to/migrations');
}
Views
$this->loadViewsFrom(__DIR__.'/path/to/views', 'courier');
Commands
Public Assets
The Service Container
https://laravel.com/docs/5.6/container
Introduction
For managing class depencies and performing dependency injection.
public function __construct(UserRepository $users)
- Easy to swap it out.
- Easy to mock.
Bindings
Simple Bindings
$this->app->bind('HelpSpot\API', function ($app) {
return new HelpSpot\API($app->make('HttpClient'));
});
Binding a Singleton
$this->app->singleton('HelpSpot\API', function ($app) {
return new HelpSpot\API($app->make('HttpClient'));
});
Once a singleton is created, the same object will be returned on subsequent calls.
Binding Instances
- You may bind an existing instance to the container
$api = new HelpSpot\API(new HttpClient);
$this->app->instance('HelpSpot\API', $api);
Binding Primitives
$this->app->when('App\Http\Controllers\UserController')
->needs('$variableName')
->give($value);
Binding Interfaces To Implementations
$this->app->bind(
'App\Contracts\EventPusher',
'App\Services\RedisEventPusher'
);
Contextual Binding
Two classes from same interface. Just add two different bindings.
$this->app->when(PhotoController::class)
->needs(Filesystem::class)
->give(function () {
return Storage::disk('local');
});
Tagging
$this->app->bind('MemoryReport', function () {
//
});
$this->app->tag(['SpeedReport', 'MemoryReport'], 'reports');
You can then bind the tagged ones:
$this->app->bind('ReportAggregator', function ($app) {
return new ReportAggregator($app->tagged('reports'));
});
Resolving
Using Make
$api = $this->app->make('HelpSpot\API');
//or
$api = resolve('HelpSpot\API');
Automatic Injection
public function __construct(UserRepository $users)
Container Events
$this->app->resolving(function ($object, $app) {
// Called when container resolves object of any type...
});
Service Providers
https://laravel.com/docs/5.6/providers
Service providers are where things are registered:
container bindings, event listeners, middleware and routes.
php artisan make:provider RiakServiceProvider
Writing Service Providers
only bind things into the service container ** **never attempt to register any event, routes etc within the register method (you may accidentally use a service that is provided by a service provider which has not loaded yet.)
All have a register and boot method.
Register
Only bind things into the Service Container
define an implementation of Riak\Connection in the service container
public function register()
{
$this->app->singleton(Connection::class, function ($app) {
return new Connection(config('riak'));
});
}
When to use a service provider?
From https://laracasts.com/lessons/service-providers-decoded
** IOC container is the application **
Can bind, useful when you have dependencies:
$filesystem = new Illuminate\Filesystem\Filesystem(new Foo, new Bar(new Baz));
This is cumbersome. Can be done once in a service provider:
public function register()
{
$this->app->bindShared('files', function() {return new Filesystem(new Baz, new Bar, new Foo)});
}
This will enable us to do this:
$filesystem = $app['files'];
Quick example
Foo needs Bar and Baz:
Instead of:
$foo = new Foo( new Bar, new Baz)
Can use:
App::bind('Foo', function()
{
return new Foo(new Bar, new Baz)
} );
dd(App::make('Foo'))
The app binding can then go in a service provider.
This is all just about resolving depencies.
Imagine you have created a class which requires multiple dependencies and in general you use it like this:
$foo = new Foo(new Bar(config('some_secret_key')), new Baz(new Moo(), new Boo()), new Woo('yolo', 5));
it’s doable, but you wouldn’t want to figure out these dependencies every time you try to instantiate this class. That’s why you want to use service provider where in the register method you can define this class as:
$this->app->singleton('My\Awesome\Foo', function ($app) {
return new Foo(new Bar(config('some_secret_key')), new Baz(new Moo(), new Boo()), new Woo('yolo', 5));
});